Urine drug testing is widely used for testing for opioids and illicit drugs. There are two types of urine drug testing: a screening test and a confirmatory test. The screening test uses an immunoassay to look for the parent drug and/or metabolite. Most UDTs screen for cocaine, marijuana, PCP, opiates, amphetamines, while some also test for benzodiazepines and methadone. The confirmatory urine drug test is done by gas Chromatography/mass spectrometry or high-performance liquid chromatography; this test is highly specific and is typically used when testing for the presence of a specific drug is needed.
Why urine drug testing?- - monitor pharmacotherapy compliance;
- - identify individuals who may be at high risk;
- - a means of providing documentation to an agreed treatment plan.
- temperature 90° F to 100 ° F
- pH 4.5 – 8
- creatinine concentration > 20 mg/dl
- specific gravity 1.003 – 1.030
Creatinine adjusted drug levels
The measured drug level is adjusted to the level of creatinine detected and multiplied by 100 mg/dl (patient's directly measured THC level x average creatinine excreted ÷ patient’s directly measured creatinine level = creatinine adjusted drug level).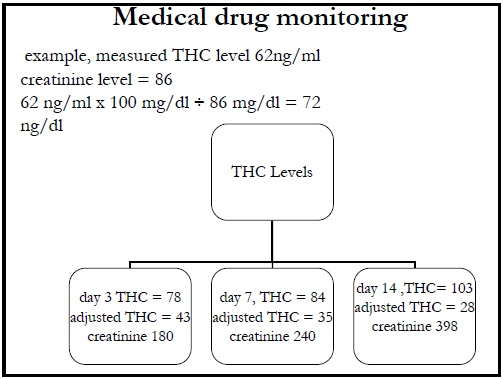
- Immunoassay drug tests
- clarifies a substance as being present or absent;
- advantages:
rapid turn around time;
inexpensive;
high sensitivity; - limitations:
cross-reactivity. - Point of care testing
- commercially available;
- does not require instrumentation;
- easy to use;
- limited number of tests;
- interpretation subjective;
- limited or deficient quality control.
- POCT testing
- users of POCT devices should understand limitations;
- used should be trained;
- be aware of interferences from chemicals;
- consider cutoff(s) in selection of device;
- must use quality control material National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry (NACB).
- Confirmatory testing
- gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS):
- the gold standard;
- highly specific and sensitive.
Drugs and their metabolites
| Drug class | Drug | Drug and/or metabolite |
|---|---|---|
| opiate | hydrocodone | hydrocodone hydromorphone |
| benzodiazapine | alprazolam | alprazolam
alphahydroxylalprazolam |
| cocaine | cocaine | benzoylecgonine |
Interpreting urine drug levels
- urine drug levels don’t indicate strength of drug being used
- urine drug levels don’t indicate how frequently the drug is used
- blood alcohol as a model
Urine drug test report
Drug not detected may be due to the following:
- patient didn’t take any of the medication;
- patient has not recently taken any of their medication;
- patient excretes medication and /or their metabolites at a different rate than normal;
- the test used was not sensitive enough;
- clerical error.
| Detection times of drugs in urine | ||
|---|---|---|
| Cutoff (ng/ml) | Days | |
| Amphetamines | 1000 | < 5 |
| Benzoylergamine after street doses of cocaine | 300 | 2-3 |
| Cannabinoids moderate smoker heavy smoker chronic smoker | 50 50 50 | 5 10 < 28 |
| Opiate | 2000 | 1-2 |
The urine test is very reliable and is performed at most federally mandated facilities that require drug testing.

No comments:
Post a Comment